
When a parent company acquires a subsidiary, any excess purchase price over the fair value of the subsidiary’s net assets is recorded as goodwill. Goodwill represents intangible assets like brand recognition, customer relationships, intellectual property, and other factors that contribute to future earnings potential. Understanding consolidated financial statements is crucial, yet often confusing, for anyone analyzing or managing Accounting for Churches a corporation. The manual complexity of financial consolidation limits accurate financial performance insights and hinders strategic, forward-thinking initiatives.

How to Prepare Consolidated Financial Statements: Examples
The goal is to ensure that the consolidated financial statements do not include profits, losses, or capital that result from transactions within the group. For organizations operating across multiple countries, foreign exchange conversion is a critical part of the financial consolidation process. When consolidating financial statements, finance teams must translate the financial data of foreign subsidiaries into the parent company’s reporting currency. This step ensures consistent presentation of all financial information, enabling aggregation and meaningful analysis at the group level. So in summary, consolidated financial statements give investors and stakeholders a complete picture of a parent company and its subsidiaries as a single reporting entity. This provides greater transparency into the overall financial health and performance of the consolidated group of companies.

Diversity, Equity & Inclusion
The proportionate consolidation method is used when a company owns more than 50% of another entity but wishes to avoid full consolidation. It involves adding the subsidiary’s proportionate share of assets, liabilities, revenues, and expenses to the parent company’s financial statements. This method is unearned revenue often used in cases where the subsidiary’s activities are substantially different from the parent company’s primary business. In consolidated accounting, the information from a parent company and its subsidiaries is treated as though it comes from a single entity. The cumulative assets from the business, as well as any revenue or expenses, are recorded on the balance sheet of the parent company.
Deconsolidation and Subsidiary Disposal
- By adjusting for these gains or losses, the consolidated financial statements provide a more accurate picture of the group’s financial position and results of operations.
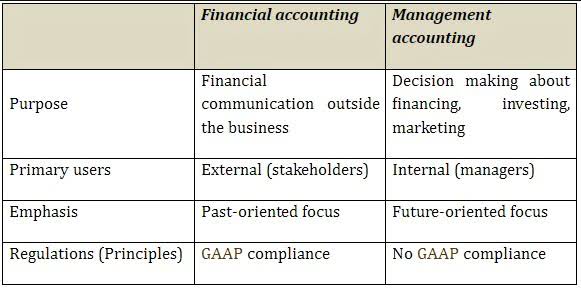
- The financial information should be in accordance with the applicable accounting standards, such as Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- In summary, consolidated statements are vital for public companies with subsidiaries and acquisitions.
- In the context of financial accounting, the term “consolidate” often refers to the consolidation of financial statements wherein all subsidiaries report under the umbrella of a parent company.
- The subsidiary’s revenue, liabilities, profits, losses, etc., are consolidated with the parent’s.
Consequently, practitioners have often reorganized it within their interpretive guidance to facilitate its application. In addition, some stakeholders have indicated that certain terms and concepts in ASC 810 are overly complex and should be clarified. The entity is structured with disproportionate voting rights, and substantially all of the activities are conducted on behalf of an investor with disproportionately few voting rights. IFRS Sustainability Standards are developed to enhance investor-company dialogue so that investors receive decision-useful, globally comparable sustainability-related disclosures that meet their information needs.
- Understanding consolidation accounting is vital for successful financial modeling and for presenting a clear financial picture of a company and its subsidiaries.
- The consolidation process can be time-consuming and complex, especially for organizations with multiple subsidiaries or complex ownership structures.
- Also referred to as amalgamation, consolidation can result in the creation of an entirely new business entity or a subsidiary of a larger firm.
- Certain services may not be available to attest clients under the rules and regulations of public accounting.
- Explore the foundational concepts and methods of consolidation accounting to accurately reflect financial positions in group entities.
- Intercompany transactions occur when entities within the same corporate group engage in financial activities with each other.
Reporting intercorporate interest—investments in common stock

The consolidation method of accounting, governed by rules such as GAAP and consolidation accounting IFRS, ensures accurate and meaningful financial reporting. With consolidation accounting, the income statement is a critical component of the consolidated financial statements. It reflects the revenues and expenses of both the parent company and its subsidiaries, providing insight into the overall profitability of the consolidated entity. The income statement must adhere to the chosen consolidation method, whether it’s the equity method, proportionate consolidation, or full consolidation.
